几个单词几句话看得不大明白?
A 79-year-old female with history of hypertension and right-sided subdural hemorrhage status-post right hemicraniectomy and cranioplasty presented to the emergency department with progressive head and focal right arm twitching concerning for a focal seizure. A head CT was obtained and is shown in the figure that follows.
79岁女性,有高血压、右侧硬脑膜下出血右半颅骨摘除术、颅骨成形术后病史,因进展性头部和右臂局灶性抽搐到急诊,头颅CT检查如下图所示。
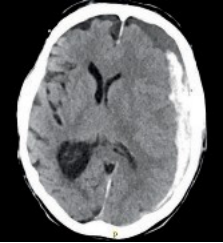
The head CT above demonstrates an acute on subacute left-sided subdural hemorrhage with left-to-right midline shift and compression of the left lateral ventricle and potential trapping of the right lateral ventricle. The timing of the subdural hemorrhage is based on the density of the blood product. Acute blood appears hyperdense to brain parenchyma. After approximately 3 days the blood product begins to break down and will reach an isodense characteristic compared to brain parenchyma, typically around 10 to 14 days. After 21 days, the blood product becomes hypodense to brain tissue and is similar to cerebrospinal fluid. The herniation demonstrated on this image is subfalcine with left frontal lobe shift under the falx into the right hemisphere. Subfalcine herniation results with cingulate gyrus herniation across the falx and compression of the pericallosal arteries resulting in contralateral (and commonly bilateral) leg weakness. Transtentorial or uncal herniation occurs with the medial temporal lobe and uncus compresses the ipsilateral cerebral peduncle resulting in compression of the ipsilateral third cranial nerve resulting in an enlarged and fixed or sluggishly reactive pupil and contralateral weakness. Tonsillar herniation occurs when there is a pressure within the cerebellum resulting in herniation of the cerebellar tonsil into the foramen magnum and compression of the fourth ventricle resulting in noncommunicating hydrocephalus and obtundation. Fungating herniation occurs when there is a skull defect and herniation of brain tissue outside the cranial vault. All herniation occurs due to a pressure gradient from one compartment (left-right hemisphere, or supra-infratentorial compartment).
上述的头颅CT显示:亚急性左侧硬膜下出血急性发作、压迫左侧侧脑室、中线左向右移位、右侧脑室有潜在的压迫。根据CT显示的血凝块密度判断硬膜下出血的时间。急性出血在脑实质中表现为高密度。大约3天后,血凝块开始分解,通常在10~14天左右达到与脑实质相等密度。21天后,血凝块密度低于对脑组织,与脑脊液相似。图示大脑镰下疝,左额叶下移位至右半脑。镰下疝合并横跨镰的扣带回疝,压迫胼胝体周围动脉,导致对侧(通常是双侧)下肢无力。小脑幕切迹疝或钩回疝发生在内侧颞叶,钩回压迫同侧大脑脚,引起同侧第三对颅神经受压,导致瞳孔扩大并固定或反应迟缓,对侧无力。当小脑受到足以导致小脑扁桃体疝入枕骨大孔的压力和存在能引起非交通性脑积水和闭塞的第四脑室压迫时,就会发生小脑扁桃体疝。当颅骨缺损和脑组织向颅顶外突出时,就会发生蕈伞样颅骨骨窗疝。所有的疝都是由于腔室(左—右半脑、或幕上—幕下脑室)的压力梯度所致。
理解的对吗?谢谢
最后编辑于 2022-10-09 · 浏览 997
















































