医学英语视听(七)

Gastrointestinal anatomy and physiology
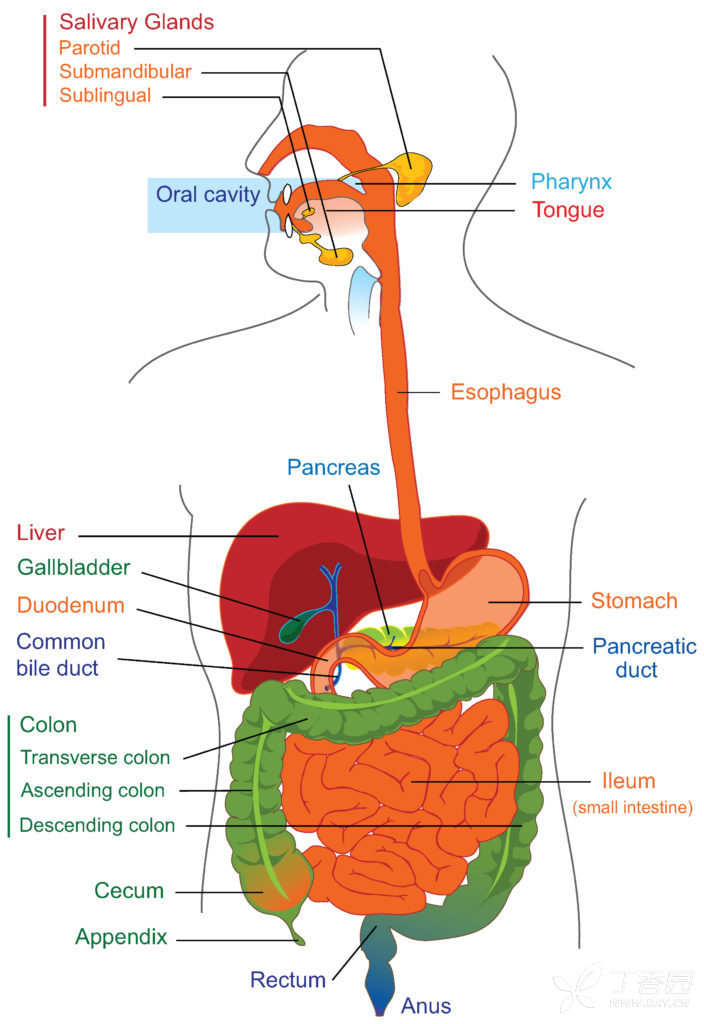
The gastrointestinal tract consists of a long tube that food travels through, which runs from the mouth to the anus, as well as to a number of helpful accessory organs that sprout off the size of that tube. The GI tract is made up of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and finally the anal canal. The accessory organs include the teeth, tongue, salivary gland, the liver, gallbladder, and the pancreas. The main job of the GI system is ingestion-taking in food, digestion- breaking it down into nutrients, absorption- pulling these nutrients into the bloodstream, and finally, excretion- getting rid of waste.
All right, so let's say we eat a slice of pizza. The pizza goes in our oral cavity where we use our teeth to masticate, or chew the food up into small fragments. These fragments get tasted and rolled around by the tongue which is basically a huge muscle that lines the floor of the mouth. The roof of the mouth, which separates it from the nasal cavity, is made up by the anterior hard palate which provides a hard surface for the tongue to mash food against, and the posterior hard palate which moves together along with the pendulum-like uvula, to form a flap or valve that helps make sure food flows down instead of going up into the nose. At the same time, the three sets of salivary glands- the sublingual below the tongue, the submandibular below the mandible, and the parotid gland which is near the ear, all secrete saliva to lubricate the food. The saliva helps to compact the food down into a soft warm ball, called a bolus. Saliva also contains salivary amylase, an enzyme that breaks long carbohydrates down into smaller sugars. Once the bolus of food gets swallowed through the pharynx, it goes into the esophagus. Right at the moment, there's a spoon- shaped flap of cartilage called the epiglottis, which acts like a lip and seals the airway off, so that the food doesn't end up in the lungs by accident.(continued...)
1. Gastrointestinal tract 消化道
词根:gastro- 胃
intestino- 肠道
-al 形容词形式
联想:gastritis 胃炎(-itis炎 )
gastric 胃的
gastric mucosa 胃粘膜
gastric ulcer 胃溃疡
gastric carcinoma 胃癌
gastrectomy 胃切除术(-ectomy 切除术)
small intestine 小肠
intestinal mucosa 肠粘膜
intestinal obstruction 肠梗阻
intestinal perforation 肠穿孔
3. Accessory organ 附属器官
联想:accessory nerve 副神经
4. Salivary gland 唾液腺
联想:Saliva 唾液
adrenal gland 肾上腺
thyroid gland 甲状腺
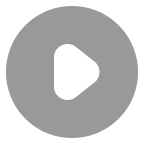
5. Liver 肝
词根:hepato- 肝脏
联想:hepatocyte=liver cells 肝细胞
hepatic portal vein 肝门静脉
hepatic artery 肝动脉
liver fibrosis/cirrhosis/failure 肝纤维化/硬化/衰竭
hepatitis A/B/C/D/E 甲/乙/丙/丁/戊肝
hepatectomy 肝切除术
hepatocarcinoma 肝细胞癌(tumor 瘤,carcinoma癌)
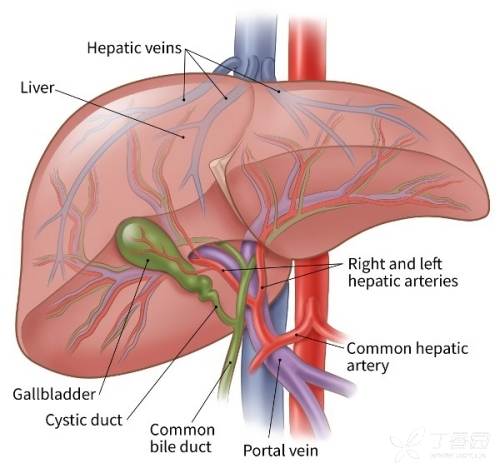
6. Gallbladder 胆囊
词根:cholecysto-
联想:cholecystitis 胆囊炎
cholecystectomy 胆囊切除术
gallstone 胆囊结石
7. Pancreas 胰腺
联想:pancreatitis 胰腺炎
8. Ingestion 摄入,digestion消化,absorption吸收,excretion排泄
9. Masticate 咀嚼
10. Pendulum 钟摆
11. Uvula 悬雍垂
12. Sublingual 舌下,submandibular 颌下,
前缀:sub- 下
联想:subcutaneous 皮下
suborbital nerve 眶下神经
词根:glosso- 舌
联想:glossopharyngealnerve 舌咽神经
词根:mandible下颌骨
联想:maxilla上颌骨
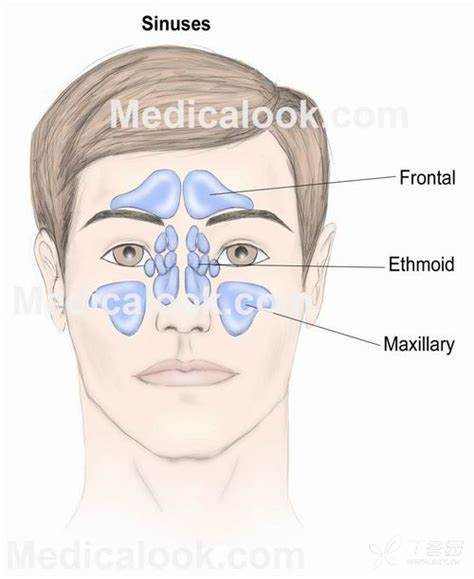
maxillary sinus 上颌窦
frontal sinus 额窦
sphenoid sinus 蝶窦
ethmoid sinus 筛窦
paranasal sinus 鼻旁窦
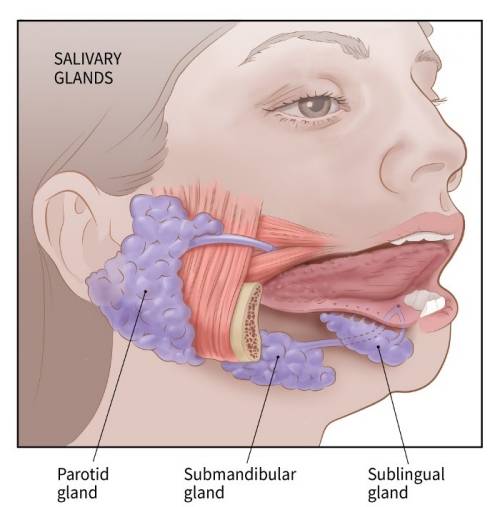
13. Parotid gland 腮腺
联想:mumps 腮腺炎(我们老家叫猪头风)
measles 麻疹
rubella 风疹
MMR vaccine 腮腺炎麻疹风疹三联疫苗
14. Lubricate 润滑
15. Bolus 食糜团
16.Amylase 淀粉酶
联想:glucose葡萄糖
fructose 果糖
lactose 乳糖
galactose 半乳糖
starch 淀粉
lactate dehydrogenase 乳糖脱氢酶