GSEA原理以及软件的运行以及常见的错误及解决办法
 推荐
推荐第一部分 GSEA原理
目标:预先定义的基因集S是否随机的分布在排序的基因list
1. 表达谱,样品分为两类,以1/2定义
GSEA considers experiments with genomewide expression profiles from samples belonging to two classes, labeled
1 or 2.
2. 基因按照表达与分类的相关性排序
Genes are ranked based on the correlation between their expression and the class distinction by using any suitable metric
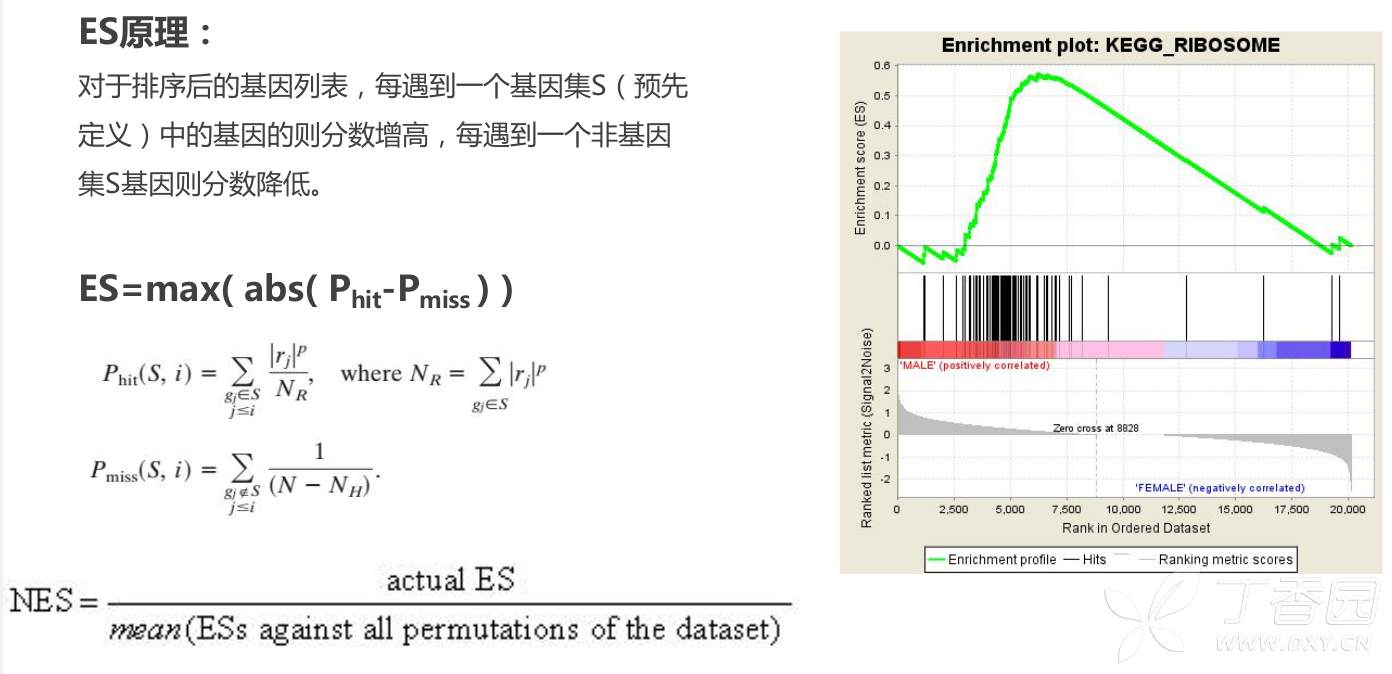
3. 计算富集打分(ES)
Given an a priori defined set of genes S (e.g., genes encoding products in a metabolic pathway, located in the same cytogenetic band, or sharing the same GO category), the goal of GSEA is to determine whether the members of S are randomly distributed throughout L or primarily found at the top or bottom. We expect that sets related to the phenotypic distinction will tend to show the latter distribution.
Step 1: Calculation of an Enrichment Score.
We calculate an enrichment score (ES) that reflects the degree to which a set S is overrepresented at the extremes (top or bottom) of the entire ranked list L.
The score is calculated by walking down the list L, increasing a running-sum statistic when we encounter a gene in S and decreasing it when we encounter genes not in S.
The magnitude of the increment depends on the correlation of the gene with the phenotype. The enrichment score is the maximum deviation from zero encountered in the random walk; it corresponds to a weighted Kolmogorov–Smirnov-like statistic
a running-sum statistic,
4. 评估ES的显著性(p值)
采用permutation :可以选择1000次,500次等
5. 多重检验校正(FDR值)
ref:
Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles
http://www.pnas.org/content/102/43/15545
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29300341/article/details/52956052